Paleo-Anthropology
Paleo-Anthropology is the study of the fossil record in order to help understand what it means to be human. This site is about how we Homo Sapiens ended up being the sole representatives of the human family and what we can learn about ourselves through the study of our evolution and that of our close relatives.
Deep, Deep Time
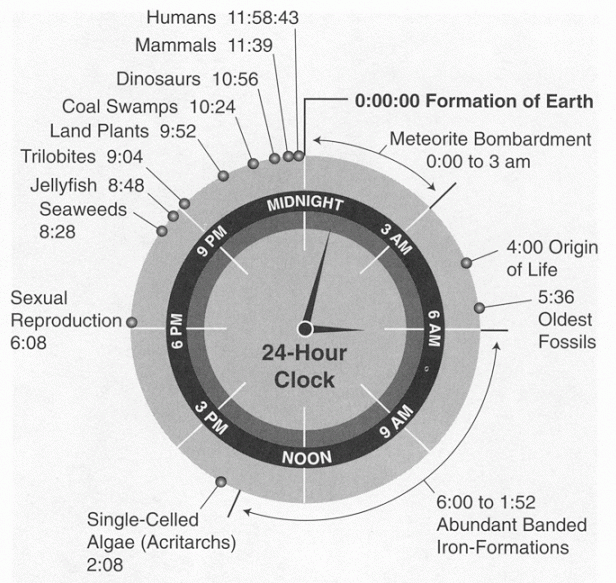
Generally speaking, we are not very good at handling big numbers. Thousands we can deal with. Tens of thousands and it starts getting a bit abstract. When dealing with hundreds of thousands upwards, the numbers quickly start to mean some version of 'lots of them' and the numbers only have relevance as ratios to other big numbers, rather than something that can be individually, visualised.
When it comes to human history, we think of civilisations, such as classical Greece, as existing a long time ago. Older time periods quickly start to merge together with images of fur clad, cave men huddled around a fire, quickly blending into some kind of monkey banging a rock, and ending up with a dinosaur walking through a swamp. But classical Greece started only 2,500 years ago (only about 100 generations back ) The cave man was largely finished with by about 7,000 years ago, whilst the rock banging monkey that we call human, started life about 2 million years ago whilst the last dinosaur died about 65 million years ago, having existed on for about 160 million years.
...Basically, us humans, have only just arrived.
BEWARE: When considering dates, remember that different environments change at different rates. Ancient societies were isolated and communication difficult. Different dating techniques can deliver different results.
Treat all dates as indicative, NOT absolute.
Stone Age
For most of the last 2 million years, humans left scant evidence of their existence. (see Humans), the further back you look, the less there is to see. Over time stuff degrades and falls apart, so there's less to find.
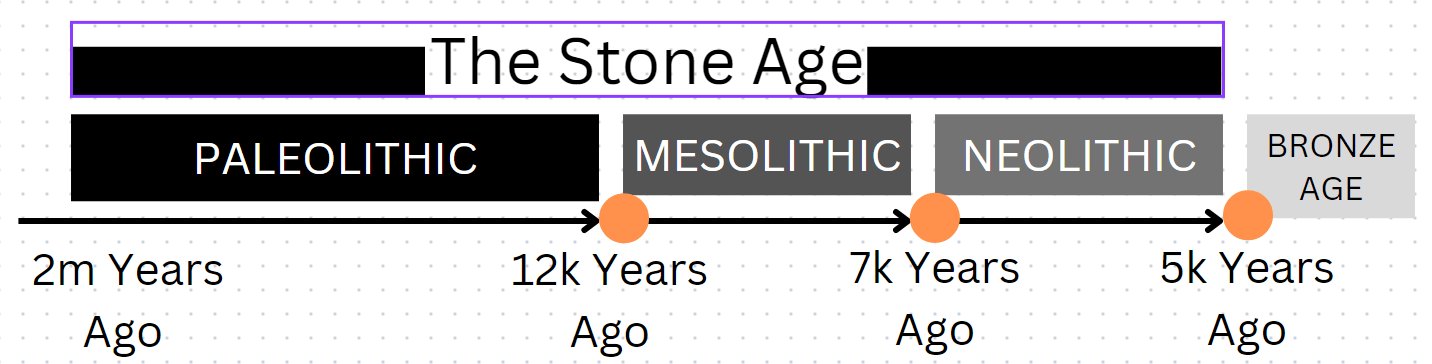
The Paleolithic is referred to as the 'Old Stone Age'. For most of it (about 1.5 million years) the only stone tool being produced and used was the hand axe. Around 400Kya (Kya = Thousand Years Ago) there was a bit of a revolution when some humans established a new way knapping flint (see Tools) which led to a range of different types of stone tool, made to a better quality.
The Paleolithic is divided into three bands delineated by their technologies and the uses that it was put to. These referred to as :
The Lower Paleolithic which was from the dawn of humans (2m years ago) up until Homo Erectus was replaced in Europe by Neanderthals. This occurred about 130Kya.
The Middle Paleolithic which followed, came to an end when Neanderthals were replaced by us, Sapiens, Modern man. This happened about 40Kya.
The Upper Paleolithic last the last stage of the old stone age which came to an end when the ice sheets of the last glacial period disappeared (see Climate) about 12Kya.
What happen next, at an ever increasing pace of societal development was the Mesolithic or Middle Stone Age, when the hunter gathers became more settle and organised, through to the Neolithic or New Stone Age which ended with Man's discovery of how to melt metals, the first phase of which was called the Bronze Age.